The Impact of Pyrolysis Oil on the Plastic Recycling Industry
This is a subtitle for your new post

Plastic pollution is one of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time. Despite global efforts to reduce plastic waste through recycling, a significant portion of plastics still ends up in landfills or the ocean due to limitations in traditional recycling methods. As the world continues to grapple with this issue, innovative solutions like pyrolysis oil are emerging as potential game-changers. By converting plastic waste into valuable fuel, pyrolysis oil technology offers a promising way to address plastic waste management, especially for plastics that are otherwise non-recyclable. In this article, we will explore how pyrolysis oil can become an integral part of the plastic recycling ecosystem, its potential to handle hard-to-recycle plastics, and how it contrasts with traditional recycling methods.
What is Pyrolysis Oil?
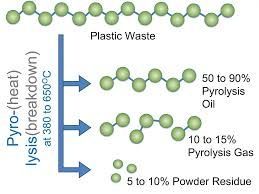
Pyrolysis oil, produced through the thermal decomposition of organic material in the absence of oxygen, is an alternative fuel source. In the context of plastic recycling, a plastic into oil machine is used to convert various types of plastic waste into pyrolysis oil, gas, and carbon black. The process involves heating plastics at high temperatures (typically 400-600°C) to break down their molecular structure, resulting in a liquid bio-oil that can be used as a renewable energy source. The byproducts of this process—gas and carbon black—have additional uses in energy generation and industrial applications.
Pyrolysis Oil and Hard-to-Recycle Plastics
One of the most significant challenges in plastic recycling is handling plastics that are difficult or impossible to process with traditional recycling methods. Common issues with conventional recycling include:
- Contamination: Plastics contaminated with food or other materials often cannot be recycled through traditional methods.
- Multi-layered Plastics: Many packaging materials are made from multiple types of plastics bonded together, which makes separation and recycling complicated.
- Non-recyclable Plastics: Certain plastics, such as polystyrene (commonly found in food containers), are not easily recyclable and often end up in landfills.
This is where pyrolysis oil technology offers a breakthrough. Unlike traditional recycling, which relies on sorting and melting plastics, pyrolysis can process a wide variety of plastic waste, including contaminated, multi-layered, and non-recyclable plastics. By using a plastic into oil machine, these materials can be efficiently converted into valuable fuel, thus reducing the burden of managing hard-to-recycle waste.
How Pyrolysis Oil Works for Plastic Waste
The process begins by feeding plastic waste into the pyrolysis reactor, where it is heated in the absence of oxygen. The heat causes the plastic to decompose into smaller molecules, which are then condensed into liquid oil. This pyrolysis oil can be refined and used as an alternative fuel in various industries, including power generation, transportation, and chemical production. Advantages of pyrolysis oil for plastic waste:
- Versatility: It can handle various types of plastic, including those that are not suitable for conventional recycling.
- Environmental Benefits: The process reduces the volume of plastic waste, helping to mitigate pollution, especially in oceans and landfills.
- Circular Economy: Pyrolysis oil contributes to the circular economy by turning waste into valuable resources that can be reused or repurposed.
Comparing Pyrolysis Oil with Traditional Recycling Methods
1. Sorting and Processing
Traditional recycling typically relies on sorting plastics by type and color, followed by mechanical processes to melt and reform them into new products. This method works well for certain plastics, such as PET (polyethylene terephthalate) and HDPE (high-density polyethylene), but struggles with plastics that are contaminated or composed of multiple layers. Pyrolysis, on the other hand, does not require sorting, making it a more efficient solution for mixed plastic waste.
2. Energy Requirements
Conventional recycling methods require significant energy inputs to melt and process plastics. While pyrolysis also requires energy to reach the high temperatures necessary for decomposition, newer technologies are increasingly efficient, with many systems capturing and reusing the energy generated during the process. This makes pyrolysis a more energy-efficient option in some cases, especially when dealing with low-quality or contaminated plastics.
3. End Products
Traditional recycling usually results in downcycled products—lower-quality materials that cannot be recycled again. For instance, a recycled plastic bottle might become a plastic chair or a lower-grade product that cannot be reused in high-end applications. Pyrolysis, however, produces valuable byproducts that can be used across a range of industries. The pyrolysis oil can be further refined into fuels or chemicals, and the carbon black produced in the process has applications in tires and pigments. This closed-loop process contributes more effectively to resource conservation than conventional recycling.
Contribution to Plastic Pollution and Resource Utilization
1. Reducing Plastic Waste
Plastic waste is a global crisis, with millions of tons ending up in landfills or the ocean each year. Pyrolysis oil technology offers a solution by converting waste plastics into usable fuel and other valuable byproducts, significantly reducing plastic pollution. Instead of being discarded or left to pollute the environment, plastic waste is given a second life in the form of energy.
2. Supporting a Circular Economy
The key to tackling plastic pollution lies in creating a circular economy where products are reused, repurposed, or recycled instead of discarded. Pyrolysis oil aligns with this model by turning waste plastic into a resource that can be reused in multiple industries. This contributes not only to waste management but also to energy production, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions.
3. Carbon Footprint Reduction
While traditional recycling methods focus on reducing plastic waste, they may still require significant energy inputs, especially when dealing with difficult-to-recycle plastics. Pyrolysis oil, when properly implemented, can help reduce the overall carbon footprint of plastic disposal. By converting plastic into oil, it not only addresses waste management but also provides an alternative to fossil fuel-based energy, further reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion: Pyrolysis Oil's Role in the Plastic Recycling Industry
Pyrolysis oil is emerging as a powerful tool in the battle against plastic waste. By utilizing plastic into oil machine, it is possible to recycle hard-to-process plastics that traditional recycling methods cannot handle. Pyrolysis offers a more efficient, scalable, and sustainable solution, contributing to the reduction of plastic pollution while providing valuable resources like bio-oil, carbon black, and syngas.
Although pyrolysis oil is not a complete replacement for traditional recycling, it serves as a vital complement—especially for the plastics that are currently discarded or polluting the environment. As technology advances and adoption grows, pyrolysis could become an essential part of the global plastic recycling ecosystem, driving both environmental and economic benefits in the process.